Charging is crucial as it aims to maximize lead-acid batteries’ performance and life. Overcharging results in higher battery temperature, higher gassing rates, higher electrolyte maintenance, and corrosion of components, while repeated undercharging leads to a gradual reduction of battery capacity, which is sometimes irreversible. To determine an effective charge procedure the relationship between the available capacity of the batteries, the overcharge applied and the DOD level before charging had to be defined. This blog will discuss the problems concerning lead acid battery overcharge, introduce the three stages of the CCCV charge method, and offer practical advice on how to avoid overcharging and prolong the battery’s life.
Understanding Lead-Acid Battery Overcharge
What is Lead-Acid Battery Overcharge?
Overcharging is the act of overcharging a battery and charging it beyond its maximum charging capacity thereby increasing voltage and current. This condition leads to severe straining of battery interior and significantly diminishing battery efficiency and life span.
Consequences of Overcharging
Charging a lead acid battery at high temperatures can cause serious damage to the battery and even lead to explosions. When a battery is overcharged, it may experience:
- Reduced Battery Life: Exaggerated use increases internal resistance, reducing the number of cycles performed.
- Potential Damage: Inadequate voltage from the alternator stator may also cause the battery voltage to increase to dangerous levels and this would result in the heating of the battery and physical damage to the battery in the form of warped plates or melted separators.
- Safety Hazards: Buying more gas than necessary leads to risk of leakages and blockage with a possibility of explosion.
In extreme cases, overcharging may also result in an explosion or fire, which can be hazardous to users.
How to Properly Charge Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries may be charged with the CCCV charge method which is a multi-step charging procedure assuring the battery is fully charged without overcharging and degrading it. This method involves the following three stages: Constant-Current Charge, topping charge, and float charge.
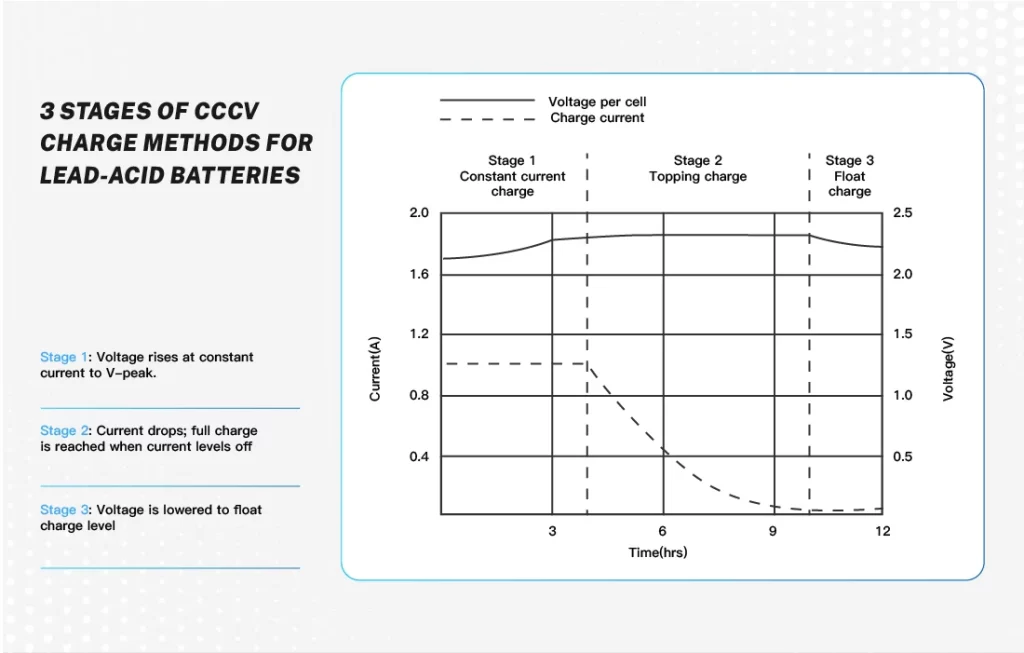
Stage 1: Constant-Current Charge
- During this stage, a constrained steady current is administered onto the battery causing the terminal voltage to increase.
- The battery charges from 0% to 70% of its capacity.
- This stage indeed takes 5-8 hours.
Stage 2: Topping Charge
- When the battery cell reaches its upper charge voltage setting, the current starts falling off as a result of saturation.
- A much lower charge current is applied in the remaining 30% of the charge as required for saturation.
- This stage may take another 7-10 hours.
- The topping charge is very important for the battery since the lack of this stage causes sulfation – a process that impairs the battery’s functioning capacity and effective life.
Stage 3: Float Charge
- After the topping charge, a float charge is added to it to keep the battery charged at 100% of full rating.
- The float charge serves as the offset for the self-discharge which is inherent in all cells.
- At this time the float voltage is lowered to the level which ensures minimal water evaporation and grid discoloration.
The first stage of charging from the constant current charge to the topping charge moves automatically to stage 2 when the battery reaches the battery voltage set at stage 1. This current then starts to decrease as the battery is beginning to approach the state of being saturated. Charging is deemed complete when the current tapers off to 3- 5% of the Ah specification.
The plateau timer will be employed in order to stop the charging of the battery if the leakage is high or if the low saturation current fails to be attained. The total charge time for lead-acid batteries using the CCCV method is usually 12-16 hours depending on the battery size but may be 36-48 hours for large batteries used in stationary applications. Using multi-stage charge methods and elevated current values can cut battery charge time to the range of 8-10 hours, yet without charging the toy to topping levels.
But it is important to note that lead-acid batteries cannot be charged any faster than this system charges them and CCCV is an acceptable choice because it is slow and safe for the batteries.
How to Properly Charge Lead-Acid Batteries
Understanding Manufacturer Guidelines
Dedicate full attention to the instructions for charging voltage and current of the manufacturer. For different battery models, certain conditions must be ensured in order to avoid overcharging.
Using Proper Charging Equipment
Choose an effective and powerful charger produced specifically for lead-acid batteries. Smart chargers are especially useful because they intelligently regulate the charging process and regulate the level of charge so as not to overcharge the battery.
Monitoring Charge Levels
Do not forget to check the battery charge with a voltmeter or a battery management system from time to time. Monitoring of voltage and current counts will prevent overcharging.
| Battery Type | Charging Voltage (V) | Float Voltage (V) |
|---|---|---|
| 12V Lead-Acid | 14.4 – 14.8 | 13.2 – 13.8 |
| 6V Lead-Acid | 7.2 – 7.4 | 6.6 – 6.9 |
Table: Ideal Voltage Levels for Lead-Acid Batteries
How to Prevent Lead-Acid Battery Overcharge
Smart Charging Techniques
Smart charging machines are charged using microprocessors that control and regulate the charging process in such a way can ensure not overcharge the battery.
Battery Management System
A good BMS suitable for lead acid batteries will oversee and manage the charging of batteries and at the same time ensure overcharging does not occur.
Regular Maintenance
Incorporate a regular maintenance check once in a while; for instance, the terminals should be checked for dust and the connectors ought to be cleaned while the electrolyte levels should be measured. Maintenance m is important in preventing overcharging because it allows for identifying possible causes of overcharging before it takes place.
Environment and Usage Considerations
Do not charge the battery near the source of direct heat or cold as fluctuations in temperature can affect the charging of the battery. More importantly, charge the battery properly, don’t let it drain too much and don’t overuse it, thereby overcharging it during the recharge process.
Ensure Battery Longevity with Mokoenergy’s BMS
Mokoenergy provides an intelligent Battery Management System (BMS) that is tailored to increasing the performance and durability of lead-acid batteries. The BMS also ensures safe and accurate charging for the battery through constant monitoring.
Features:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Tracks voltage, current, and temperature.
- Automated Control: Adjusts charging parameters to prevent overcharge.
- Fault Detection: Identifies and alerts users to potential issues.
Mokoenergy’s BMS employs intelligent algorithms to maintain optimal charging conditions. It constantly checks the condition of the battery and prevents the battery from overcharging as well as increases safety and reliability and ensures longer battery lifespan. Knowing when batteries are being overcharged and practicing the correct way of dealing with batteries can avoid damaging your battery and help prolong the life of your battery. Some advanced tools like BMS devices from Mokoenergy can also help in maintaining battery health more easily. Interested in your business? Click here to reach our specialists!
You may also like