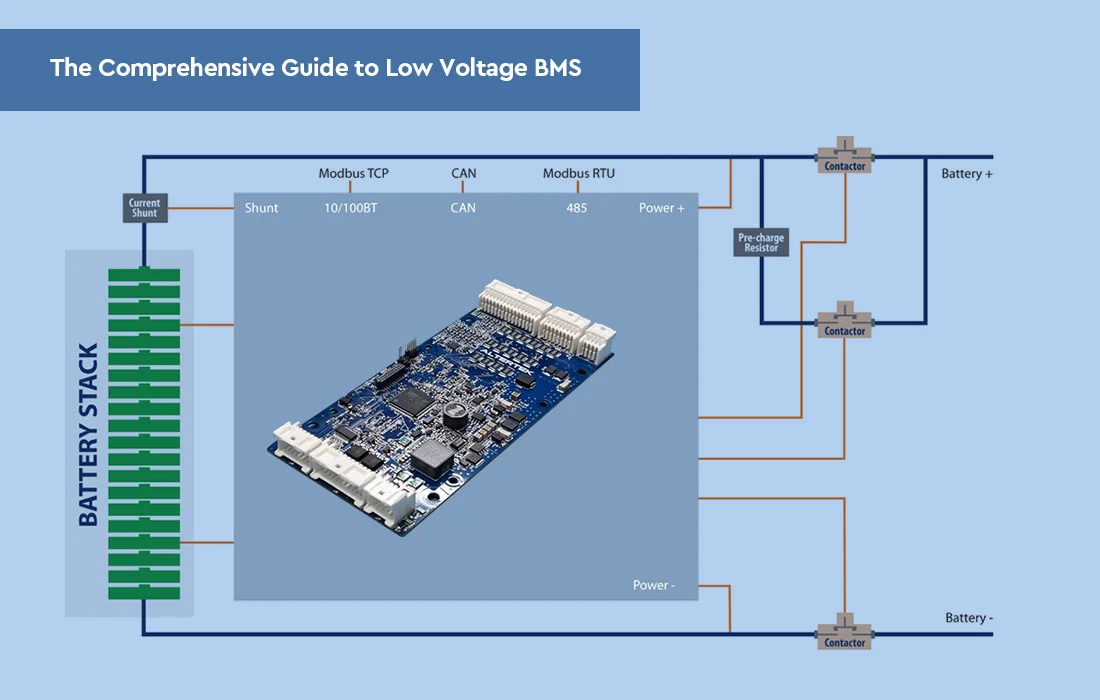
Here is a comparison table outlining the advantages and ideal use cases for the CAN bus, Modbus, and RS-485 for BMS communication protocol in the context of a BMS board:
| Protocol | Description | Advantages | Ideal Use Cases |
| CAN bus | A robust vehicle bus standard designed to allow microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other within a vehicle without a host computer. | – High speed (up to 1Mbps) – Priority-based messaging – Robust in noisy electrical environments | – Electric vehicles – Hybrid vehicles – Advanced BMS with many modules/cells |
| Modbus | A serial communications protocol was published by Modicon in 1979 for use with its programmable logic controllers (PLCs). | – Mature and widely adopted – Simple and easy to implement – Publicly available specifications | – Industrial automation and control systems – Building automation – Basic BMS systems |
| RS-485 | A standard defining the electrical characteristics of drivers and receivers for use in balanced digital multipoint systems. Supports multi-drop connectivity. | – Inexpensive – Excellent noise immunity over long distances – Supports up to 32 nodes per master | – Long cable runs – Networks spread over large areas – Cost-sensitive BMS |
In a summary,
- CAN bus is fast and ideal for advanced BMS in electric vehicles
- Modbus is simple, mature, and good for basic industrial BMS
- RS-485 works over long distances and is cost-effective
The best BMS communication protocol depends on your specific requirements like speed, number of nodes, noise immunity, costs etc. Let me know if you need any other details!