In the rapidly evolving world of electric vehicles (EVs), battery health is paramount. As the power source for EVs, batteries are subjected to various stressors over time, leading to a phenomenon known as “battery degradation.” Understanding what it is, its causes, and how to mitigate it is crucial for maximizing the lifespan and performance of EVs. This blog delves into the intricacies of this term, offering insights into how to prevent it from adversely affecting your vehicle’s efficiency.
I. What Is Battery Degradation?
Battery degradation refers to the gradual loss of a battery’s ability to hold a charge or deliver power effectively over time. It’s a natural process that occurs as the battery undergoes repeated charge and discharge cycles. As batteries degrade, they lose capacity and efficiency, ultimately leading to reduced performance in electric vehicles.
In simple terms, it is the wear and tear that occurs within a battery over time, causing it to degrade in its functionality. For EV owners, understanding battery degradation is vital for maintaining vehicle performance and extending the battery’s lifespan.
II. What Happens When Battery Degradation Occurs?
When a battery degrades, its performance diminishes, which can have several consequences:
- Reduced Range: One of the most noticeable effects of battery degradation is a decrease in the range of an EV. As the battery degrades, it can’t store as much energy, meaning the vehicle can’t travel as far on a single charge.
- Longer Charging Times: Degraded batteries may take longer to charge because they can’t absorb energy as efficiently as when they were new.
- Power Loss: A degrading battery might not be able to deliver the same level of power, resulting in sluggish acceleration and reduced overall performance.
- Increased Costs: As a battery degrades, it may need to be replaced sooner than anticipated, leading to additional costs. Additionally, a degraded battery can reduce the resale value of an EV.
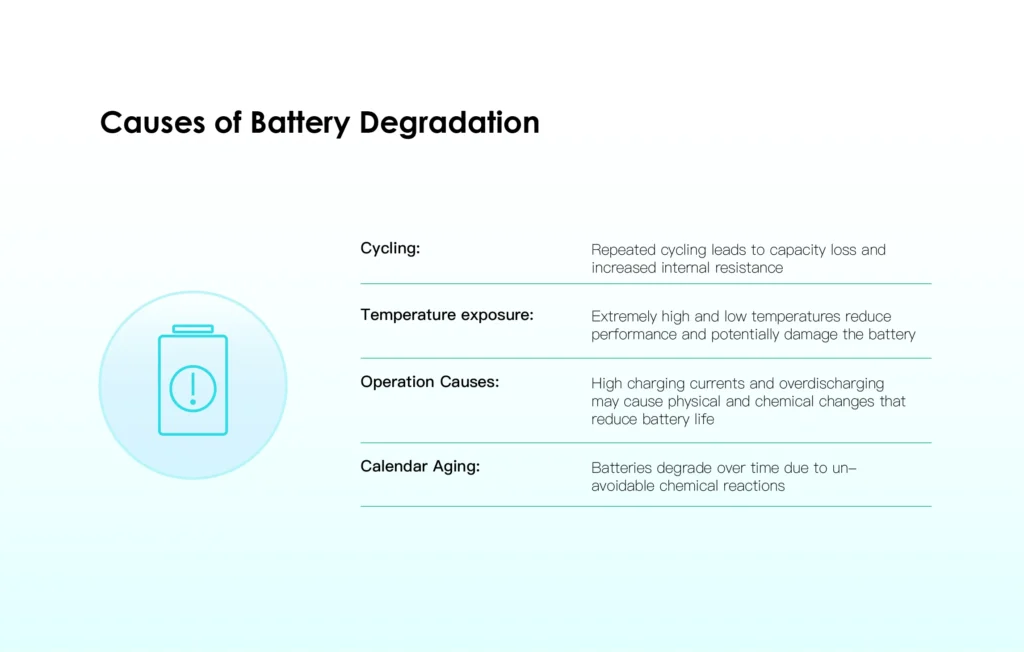
III. Causes of Battery Degradation
Understanding the factors that contribute to battery degradation is essential for preventing it. Here are the primary causes:
1. Cycling
Every time a battery goes through a charge-discharge cycle, it undergoes some level of stress. This process, known as cycling, is one of the most significant contributors to battery degradation. Over time, repeated cycling can wear out the battery’s internal components, leading to a decrease in capacity.
The more frequently an EV battery is cycled, the faster it will degrade. However, even when not in use, a battery can degrade if it’s left in a state of low or high charge for extended periods.
2. Temperature Exposure
Temperature plays a critical role in battery health. Exposure to extreme temperatures, whether hot or cold, can accelerate battery degradation. High temperatures can cause the electrolyte within the battery to break down, leading to a loss of capacity. On the other hand, cold temperatures can slow down the chemical reactions within the battery, reducing its ability to hold a charge.
Inconsistent temperature management can result in uneven degradation across the battery cells, leading to reduced overall efficiency and performance.
3. Operation Causes
The way a battery is used can also affect its lifespan. Factors such as frequent fast charging, discharging to very low levels, and maintaining a high state of charge (SoC) can all contribute to accelerated battery degradation.
For example, while fast charging is convenient, it generates more heat and stresses the battery more than standard charging methods. Similarly, regularly discharging the battery to a very low level or keeping it fully charged for extended periods can lead to faster degradation.
4. Calendar Aging
Even when not in use, batteries degrade over time—a process known as calendar aging. This type of degradation occurs due to the chemical reactions within the battery that continue even when it’s not being cycled. Calendar aging is influenced by factors such as temperature, storage conditions, and the state of charge.
Batteries that are stored at high temperatures or left in a fully charged state for long periods are more susceptible to calendar aging. This type of degradation is inevitable, but it can be managed with proper care and storage practices.
IV. How to Mitigate Battery Degradation
While battery degradation is unavoidable, there are several strategies that EV owners can employ to mitigate its effects and extend the battery’s lifespan.
1. Temperature Control
As temperature is a significant factor in battery degradation, maintaining an optimal temperature range is crucial. Avoid exposing the battery to extreme temperatures, and whenever possible, park in shaded or temperature-controlled environments. Many modern EVs come equipped with battery thermal management systems that help regulate the battery’s temperature, reducing the risk of degradation due to thermal stress.
2. SoC Estimation
Maintaining a balanced state of charge (SoC) is another effective way to mitigate battery degradation. Avoid charging the battery to 100% or letting it discharge completely. Instead, aim to keep the SoC between 20% and 80%. This reduces stress on the battery and can significantly slow down the degradation process.
Some EVs offer features that allow users to set a maximum charge limit, helping to avoid overcharging and prolong battery life.
3. Proper Charging
The way you charge your EV can also impact battery health. Whenever possible, use standard charging methods instead of fast charging, which generates more heat and puts additional stress on the battery. If fast charging is necessary, try to limit its use to only when it’s absolutely needed.
Additionally, avoid charging the battery to full capacity if you don’t need the extra range. By charging only what you need, you can reduce the overall wear and tear on the battery.
4. Cycle Life Management
Managing the number of charge-discharge cycles the battery goes through can also help extend its life. Try to avoid unnecessary short trips that require frequent charging. Instead, plan your driving routes to minimize the number of cycles your battery goes through.
Some EVs have built-in features that help manage cycle life, such as regenerative braking systems that recharge the battery while driving, reducing the need for frequent charging.
5. Regular Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular monitoring of your EV’s battery health can help you catch any potential issues early on. Many modern EVs offer battery management systems that provide insights into the battery’s condition, allowing you to take proactive measures to mitigate degradation.
Regular maintenance, including software updates and inspections by a certified technician, can also help ensure that your battery remains in optimal condition. These updates often include improvements to the battery management system, further enhancing the battery’s longevity.
Conclusion
Battery degradation is an inevitable part of owning an electric vehicle, but with proper care and maintenance, its impact can be minimized. By understanding the causes of battery degradation and implementing strategies to mitigate it, EV owners can extend the life of their batteries, ensuring better performance and reduced costs over time. As the EV industry continues to evolve, staying informed about battery health will be key to maximizing the benefits of this sustainable mode of transportation.